Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
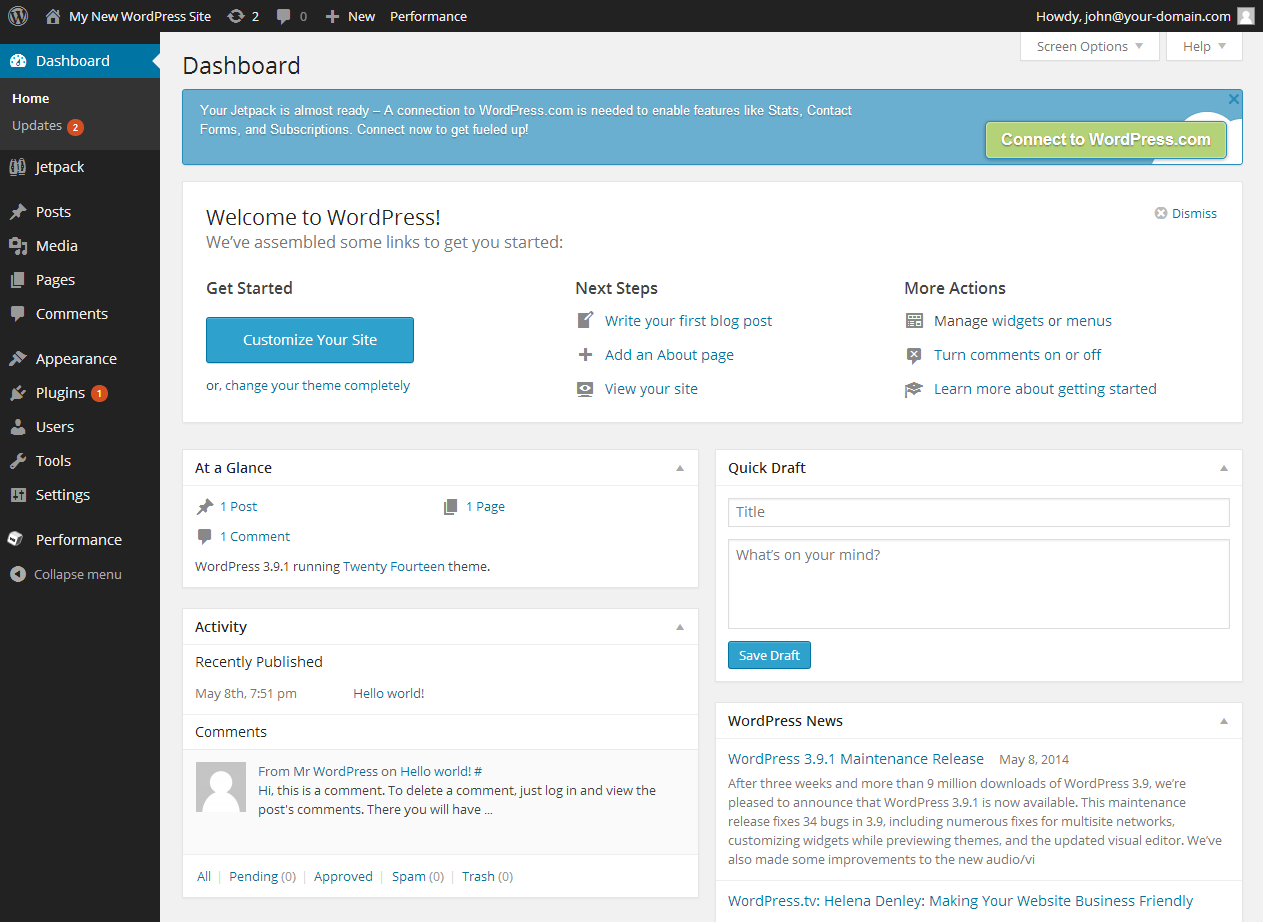
Before we dive into the intricacies of the WordPress Dashboard, let’s start with the basics: logging in. Logging into your Dashboard, you only have to add “/wp-admin” to the end of your website’s URL, your website. login to the WordPress dashboard (www.example.com/wp-admin) with your username and password. After logging in, you will be welcomed by the WordPress Dashboard, your control panel for managing your website.
Home: You will get a Dashboard page, as the default view page, which is updated in real time showing the different activities, such as latest posts, comments, and how many users visited your website.
Updates: Moreover, you can see and install core updates for WordPress, themes, and plugins to make your site running smoothly and securely.
Posts: The part of the process that might include the creation, editing, as well as managing of the blog posts is the section. Furthermore, creating categories and labeling your posts under tags will make it easier for blog visitors to explore and locate relevant information.
Media: Handle all your media files, including images, videos, and audio, once uploaded to your site. If there is any media file new, you can add it directly from here as well.
Likewise, technology has transformed the way we shop for products and services.
Pages: Like in the case of posts that are temporary, pages are also the static content that you can construct, control and edit on this section. Pages are normally used for important information such as “About Us,” “Contact,” and “Services.
Comments: Track and supervise the comments made by others in your posts and pages’ discussion board. By app, you can easily approve, reply, or delete comments.
Appearance: Make your website look special by changing themes, customizing menus, widgets, and the site’s header and background.
Plugins: Acquire functionality of your site by getting and operating plugins. Plugins help you add capabilities like contact forms, SEO optimization, and social media integration, thus your site gets improved as well.
Users: Managing user accounts and roles on your site. Things like new users creation, granting permissions with different level of access and editing current users profile are among the things you can do.
Tools: You can use the available import/export tools to import or export content as needed. Also, you can take the website’s backups and do the settings configuration.
Settings: Set general settings for your website, such as site title, URL structure, reading and writing settings, and much more.
Posts and Pages: Under the “Posts” and “Pages” names where you can add a new post or a new page by hitting the button “Add New”. The text editing tool is the same one that you might have used before. It comes with built-in features for formatting text, adding images, and adding links. You can also save drafts, see what you are publishing, and schedule posts for the future.
Media Library: The “Media” tab serves as a working folder for your media files, be it videos or pictures that you have uploaded. Once you have a media library, you can sort it using folders, search a file of your choice, and lastly, edit media details like alt text and captions.
Appearance Customization: The “Appearance” menu is where you can determine the visual appearance of your site by choosing and customizing the themes. Apart from that you can make a custom menu as well which the navigation controller of your website may follow and widgets can be added to the sidebar or footer to show more content in one place.
Plugin Management: On the “Plugins” site you can go through, install, activate, and deactivate various plugins to have more advanced features and functionality for your site. You can also keep the plugins up to date to make sure they are compatible with the newest WordPress version.
User Management: When you want to use the “Users Account” section, you interact with the user’s accounts and roles to manage your site. Adding new users and assigning them roles such as administrator, editor, writer, contributor, or subscriber is also possible. You can make desired changes to already existing roles at any stage.
Settings Configuration: The “Settings” section is where you can adjust all the settings for your site, such as the general settings like site title and tagline, the reading settings like front page display and post visibility, the writing settings like default post format and category, and the discussion settings like comment moderation and notification options.




